Introduction
From small businesses and startups to large corporations, organisations are increasingly dependent on digital infrastructure for their daily operations, making the protection of sensitive information more vital than ever.
In our extensive experience assisting clients with regulatory audits and actual security incidents, we have observed that straightforward preventative strategies can significantly reduce the risk of major data breaches. Neglecting to adopt these measures can result in substantial financial losses, harm to reputation, and potential legal repercussions.
One of the most efficient methods to establish fundamental protection in the UK is by adopting Cyber Essentials, a government-supported initiative managed by the IASME Consortium. The IASME Consortium collaborates with the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) to supervise the creation and execution of the Cyber Essentials controls, guaranteeing they remain current and effective.
Cyber Essentials outlines five fundamental and vital core controls—firewalls, Secure Configuration, User Access Control, Malware Protection, and Secure Update Management—that are easy to implement and can be applied to any device, service, or cloud platform that stores or processes business data.
Following these measures can significantly reduce your organisation’s exposure to common cyber threats while demonstrating compliance with clients, partners, and regulatory bodies through certification.
The Cyber Essentials scheme offers two levels of certification: Cyber Essentials (self-assessment) and Cyber Essentials Plus (independent testing).
Both levels require an ongoing commitment to timely patching (particularly for high/critical vulnerabilities), multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all accounts, including those hosted in the Cloud, and proactive review of security controls.
As you review each of the five controls below, consult official resources—such as the NCSC website and the IASME Cyber Essentials Knowledge Hub—for the most up-to-date guidance. If you have any questions or concerns, please schedule a call directly with an NCSC Assured Cyber Advisor at CSIQ.
What is Cyber Essentials?
Cyber Essentials is a UK Government-supported initiative aimed at assisting organisations of all sizes in protecting themselves against prevalent cyber threats.
The controls cover everything from firewall configurations to user access. Its implementation can help businesses establish a strong security baseline and bolster their confidence in the face of cyber threats.
The scheme offers two levels of certification:
- Cyber Essentials (self-assessed): You complete a questionnaire to verify that you have the required measures.
- Cyber Essentials Plus (independently tested): A qualified assessor from a Certification Body such as CSIQ conducts external and internal tests to confirm that your controls meet the standard.
Organisation Scope
Drawing from our extensive experience in helping organisations of all sizes achieve Cyber Essentials certification, we often come across devices or services operating on outdated software that is no longer supported. It’s crucial to understand that the assessment encompasses all devices, services, and cloud platforms that handle or store company data.
This scope includes remote workers’ laptops, personal devices under BYOD policies, and cloud-based services—even if they are only occasionally used for corporate tasks.
To meet scheme requirements, multi-factor authentication (MFA) for user/admin accounts and timely patching of high/critical vulnerabilities (typically within 14 days) are non-negotiable. These areas are often highlighted during the Cyber Essentials Plus audit.
In practice, maintaining these patching schedules can be one of the biggest hurdles, especially when juggling a range of on-premise, hosted and remote worker devices.
However, proven solutions—such as automated patch management or assigning a dedicated security coordinator—can significantly reduce risk and simplify the certification process.
Achieving Cyber Essentials is more than just a compliance task; it demonstrates a clear commitment to protecting client data and significantly boosting your organisation’s reputation. However, the effort doesn’t stop after meeting the requirements. It is crucial to consistently document, monitor, and periodically review your security measures to maintain ongoing vigilance, especially in today’s fast-changing threat environment.
Control 1: Firewalls
Firewalls are the first defence against unauthorised access, filtering inbound and outbound network traffic to protect sensitive systems. Under Cyber Essentials, every in-scope device—including employee laptops, BYOD endpoints, and cloud resources—must be covered by a properly configured firewall, whether working from within the office or remotely.
A recent incident response engagement showed that overlooking simple firewall best practices, like changing default credentials and preventing management from the internet, can painfully expose organisations.
By ensuring that only legitimate traffic is allowed, you can significantly reduce the attack surface without significant complexity or cost.
Key Steps to Maintaining Firewall Security:
- Disable Default Settings: Change default credentials and deactivate unnecessary administrative services.
- Review Configurations Regularly: Ensure only essential ports and services are open. Schedule audits to align with evolving needs and emerging threats.
- Stay Current on Patches: Cyber Essentials requires that high/critical-risk vulnerabilities are patched within 14 days. Keep a documented patch log to track firewall firmware updates and confirm that critical fixes are applied promptly.
- Document and Audit: Maintain a comprehensive record of firewall rules and periodically verify that they meet organisational requirements and compliance mandates.
Maintaining a Firewall Access Register will greatly simplify change management and ensure that any exposed services have a business case.
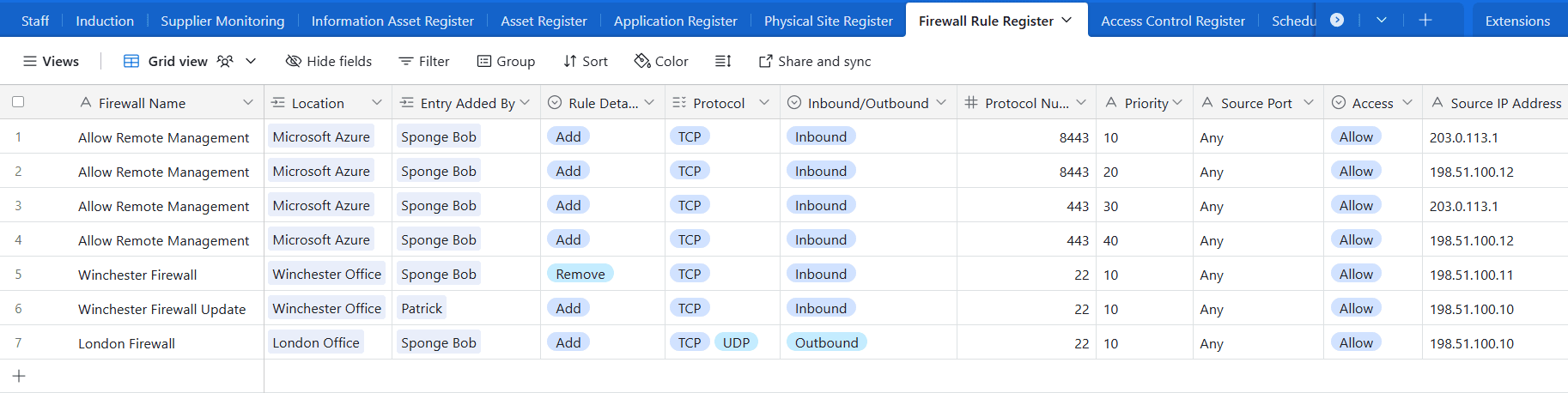
Control 2: Secure Configuration
A secure starting point for all your systems—whether on-premises servers, cloud instances, or BYOD devices—minimises vulnerabilities.
In our experience running Cyber Essentials audits, one of the most common pitfalls is leaving default configurations or unnecessary services active.
This broadens your attack surface, which can lead to opportunistic hackers deploying ransomware or attempting to commit fraud by intercepting email communication.
Key Steps to Achieve a Secure Configuration:
- Reduce the Attack Surface: Disable or remove any unnecessary software and services to limit avenues of compromise.
- Change Default Credentials: Default passwords and usernames are prime targets. To tighten security, apply multi-factor authentication (MFA), rename default accounts, and ensure that any default passwords are changed.
- Regular reviews and practical checklists when setting up new users and accounts can make secure configuration a repeatable and efficient process rather than a one-time scramble.
Control 3: User Access Control
Compromised credentials are a leading cause of data breaches, and we’ve repeatedly seen organisations overlook user access hygiene—such as leaving admin privileges on user accounts or retaining generic logins.
Under Cyber Essentials, you must strictly manage and monitor user permissions across all devices and services, including those used by remote workers and BYOD.
Key Steps for Effective Access Control:
- Assign Unique User Accounts: Avoid shared or generic logins so you can accurately track user actions.
- Apply Least Privilege: Grant employees only the access they need for their roles. This “minimum necessary” approach reduces the risk of unauthorised access or data mishandling.
- Implement a Password Policy: Use the NCSC three random word standard and a password manager to ensure that passwords remain unique and difficult to guess. Combined with MFA, this will protect your company from most phishing and internet-borne attacks.
- Review Permissions Regularly: Whenever someone’s role changes or leaves the organisation, immediately adjust or revoke their access. Schedule periodic audits to ensure ongoing compliance.
Onboarding and Offboarding policies along with an Access Register can dramatically simplify processes and risks around User Access Control.
Control 4: Malware Protection
Ransomware, spyware, and other malicious software pose an ever-present risk to organisations of all sizes.
Our recent incident response work found disabled antivirus engines and untrained IT staff are often the biggest culprits in allowing malware infections to take root.
Under Cyber Essentials, every in-scope device (including those used by remote staff or under BYOD policies) must have adequate malware defence measures.
Key Steps for Comprehensive Malware Protection:
- Deploy Reputable Antivirus/Anti-Malware Software: Install real-time protection across all devices. Windows Defender meets the requirements for Cyber Essentials; however, Apple’s inbuilt XProtect will typically fail during the Cyber Essentials Plus audit.
- Keep Definitions Updated: Automate updates to ensure your defences can tackle the latest threats—one missed update can create a significant vulnerability window.
- Restrict Unnecessary Features: Disable or limit macro-enabled documents and script execution where possible; these are common infection vectors.
- Educate Your Workforce: In our experience, targeted training (e.g., spotting phishing emails) drastically reduces click-through rates on malicious links. Consider running simulated phishing exercises to keep staff vigilant.
- Review and Update Controls Regularly: Periodically assess malware protection settings and policies, especially after discovering new threats or vulnerabilities. Centralised visibility of your endpoints and their status is essential to ensure full coverage.
Organisations can significantly curb the risk of malware-related breaches by combining robust technical safeguards with ongoing user awareness.
Control 5: Secure Update Management
imely patching is one of the simplest yet most powerful ways to reduce exposure to cyber threats.
From our incident response work, we have consistently seen that outdated or unpatched software is a prime target for opportunistic attackers.
Cyber Essentials emphasises the 14-day patching window for high or critical vulnerabilities, reflecting how crucial it is to address known weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Key Steps for Effective Secure Update Management:
- Patch High/Critical Vulnerabilities Quickly: An automated patching solution and vulnerability scanning can ensure you don’t miss critical fixes.
- Enable Automatic Updates: This minimises human error and shortens the window when systems remain vulnerable.
- Keep an Up-to-Date Inventory: List all hardware, software, and firmware so nothing slips through the cracks.
- Test Before Full Deployment: Particularly in mission-critical environments, test patches on a staging system to avoid unexpected downtime or compatibility issues.
- Maintain Clear Documentation: Monitor all patch deployments, review patch status regularly, and note any exceptions. This streamlines future audits and makes spotting gaps when new vulnerabilities arise easier.
With consistent monitoring and user training, secure update management helps ensure your organisation remains one step ahead of evolving threats.
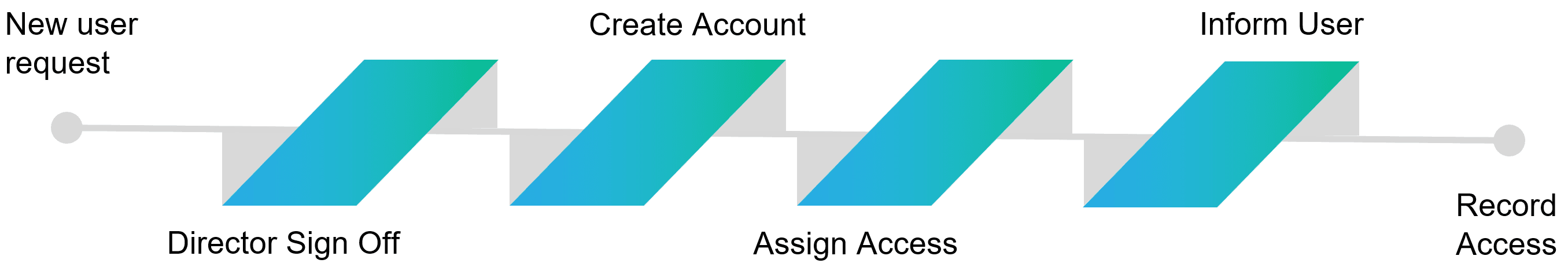
Implementing a patching cycle as outlined below can significantly reduce your risk by introducing consistency to help ensure you meet the strict patching requirements set out by the Cyber Essentials framework.

Cyber Essentials Controls In Summary
Achieving and maintaining Cyber Essentials compliance is not just a box-ticking exercise; it’s an evolving process that safeguards your organisation against a constantly shifting threat landscape.
By systematically applying the five core controls—firewalls, Secure Configuration, User Access Control, Malware Protection, and Secure Update Management—you establish a strong baseline that helps protect critical data, whether hosted on-premises or in the Cloud.
Having supported diverse organisations—from small startups to large enterprises—we’ve seen first-hand how consistent documentation, timely patch installation, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) drastically reduce vulnerabilities.
Regular audits and reviews are key to sustaining this posture: they ensure outdated configurations are caught early, privileged accounts remain safeguarded, and emerging threats are promptly addressed.
Whether you pursue Cyber Essentials (self-assessment) or Cyber Essentials Plus (independent testing), ongoing vigilance is crucial to maintaining trust with clients and partners.
If you are looking to certify your organisation to Cyber Essentials we offer solutions to meet all your needs, from help with the Self-Assessment to complete done-for-you solutions.
We openly share our pricing which can be found on our dedicated Cyber Essentials Page.
About the Author: David Pitre
David co-founded CSIQ, where he spearheads product development, technical innovation, integration, and automation—ensuring every engagement exceeds the highest standards.
As a Chartered Cyber Security Consultant (ChCSP) and NCSC Assured Cyber Advisor, he brings a deep passion for all things cyber, underpinned by extensive public and private experience.
Leveraging his IT engineering and cyber security background, David has successfully consulted, supported, and implemented technological solutions that empower businesses to thrive.
Beyond his professional endeavours, he relishes time with family, travelling, participating in charity walks, and savouring the great outdoors—particularly through his interest in viticulture.









